30+ Years of Experience in PCB Design and Manufacturing
In the rapidly evolving realm of circuit board manufacturing, both beginners and seasoned professionals face a myriad of challenges that require careful navigation. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets.com, the global circuit board manufacturing market was valued at approximately $64 billion in 2022, underscoring the significance of this industry in today's tech-driven world. As innovation continues to reshape electronics, efficiency, precision, and quality in circuit board production become paramount for success.
Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in electronics manufacturing, emphasizes the importance of adopting best practices in this competitive field: "The key to thriving in circuit board manufacturing lies in understanding both the technical intricacies and the market dynamics. Prioritizing quality while embracing innovation is essential." Her insights reflect the necessity for a strong foundation in proven techniques as well as an agile approach to new technologies.
With the intricate nature of circuit board design and production, this article outlines the top 10 tips that can enhance your circuit board manufacturing process, drawing on industry best practices that cater to both novices and experts alike. By embracing these strategies, manufacturers can not only improve their operational efficiency but also stay ahead in a market characterized by rapid change and relentless competition.

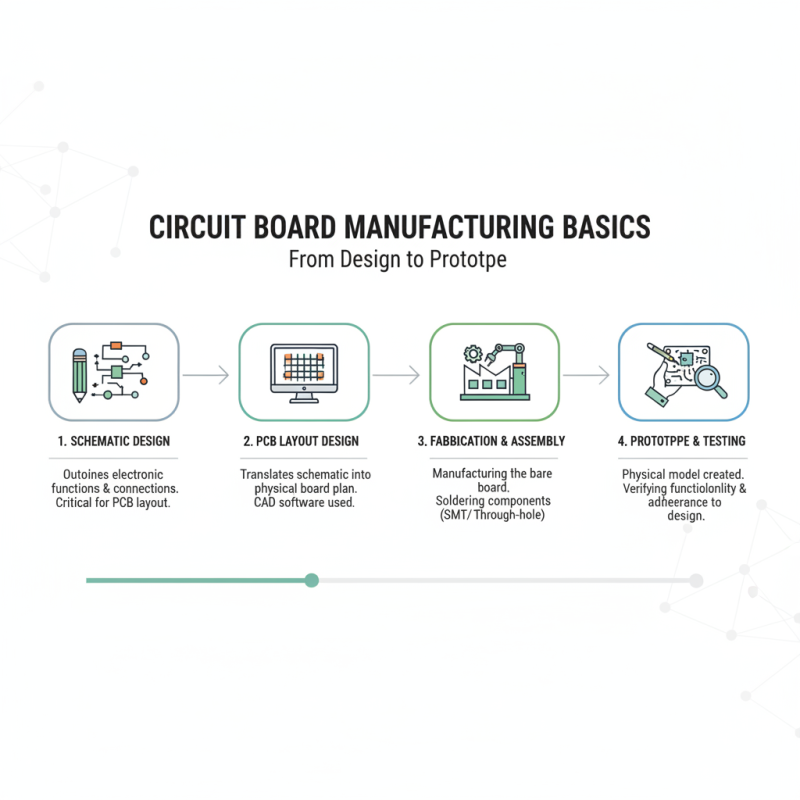
Understanding the basics of circuit board manufacturing processes is crucial for both beginners and professionals aiming to create efficient and functional electronic devices. The process typically begins with designing a schematic, which outlines the electronic functions and connections of the circuit. This design phase is critical because it directly impacts the layout of the printed circuit board (PCB). Once the design is complete, the next step involves converting the schematic into a physical prototype, which requires attention to detail and adherence to specified requirements.
After the prototype is developed, the fabrication phase begins. This involves several steps including substrate preparation, layer stacking, and etching. High-quality materials must be chosen to ensure the durability and reliability of the circuit board. Additionally, selecting the right technique for soldering components onto the PCB is vital; whether through manual soldering or automated processes like reflow soldering, it affects the overall performance of the device. Understanding these foundational processes not only helps in troubleshooting potential issues but also enhances the knowledge required for optimizing circuit board designs in the future.
When embarking on the journey of circuit board fabrication, having the right tools and equipment is paramount to achieving high-quality results. Essential tools include soldering irons, multimeters, and PCB design software, which are foundational for both beginners and seasoned professionals. According to a report by the IPC—Association Connecting Electronics Industries, nearly 90% of professionals in the electronics field emphasize the importance of precision tools to enhance accuracy and efficiency during the assembly process. Investing in high-quality tools can significantly impact the durability and functionality of the final circuit board.
Tip: Always ensure your soldering iron is the right wattage for the components being used. A 30-50 watt iron is typically ideal for most circuit board work. This ensures effective heat transfer without damaging the sensitive components, which can lead to costly errors and rework.
Moreover, setting up a clean, organized workspace cannot be overstated. A clutter-free environment not only enhances productivity but also minimizes the risk of errors related to misplaced components or tools. Research indicates that maintaining an orderly workspace can boost efficiency by around 25%, allowing for a more streamlined fabrication process.
Tip: Use anti-static mats and wristbands to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. With ESD being responsible for over 30% of all electronic failures, taking these precautions is vital for protecting sensitive circuit board components during the manufacturing process.
Designing circuit board layouts requires a blend of creativity, technical expertise, and methodical planning. As a beginner or a professional, it's crucial to start with a clear understanding of the project requirements. Begin by outlining the specifications such as size, shape, and functionality of your circuit board. This step sets the foundation for an efficient layout designed to maximize performance and minimize complications.
When working on the layout, one essential tip is to keep components placed logically close together to reduce trace lengths, thus enhancing signal integrity. Ensuring proper grounding and power distribution is also vital; utilize ground planes wherever possible to avoid noise and provide a stable reference for your circuits. Moreover, be mindful of component placement to facilitate easy soldering and accessibility during testing and repairs.
Another crucial aspect is to utilize design software effectively. Familiarizing yourself with tools that offer routing and simulation features can save you considerable time and effort in the layout process. Plan for adequate spacing between traces to prevent short circuits and consider thermal management strategies, such as the placement of heat-generating components. By following these tips, you can create circuit board layouts that are both functional and efficient.
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Level | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Understand the Basics of PCB Design Software | Beginner | High |
| 2 | Choose the Right Materials for Your Project | Beginner | Medium |
| 3 | Follow Design Rules and Standards | Professional | High |
| 4 | Optimize the Layout for Signal Integrity | Professional | High |
| 5 | Practice Component Placement Efficiency | Beginner | Medium |
| 6 | Test Your Design with Simulation Tools | Professional | High |
| 7 | Implement Proper Grounding Techniques | Professional | High |
| 8 | Select the Right PCB Manufacturer | Beginner | High |
| 9 | Keep Up with Industry Trends and Technologies | Professional | Medium |
| 10 | Document Your Process for Future Reference | Beginner | Medium |
In the realm of circuit board production, avoiding common pitfalls is crucial for both beginners and seasoned professionals. One significant mistake is inadequate planning and design validation. Rush decisions can lead to design flaws that not only increase production costs but also cause functionality issues. Taking the time to validate the design through simulations and prototyping can significantly reduce errors and enhance the overall quality of the final product.
Another frequent error arises from insufficient attention to the manufacturing specifications. Many newcomers overlook essential parameters such as material selection, layer stacking, and surface finish. Disregarding these specifications can result in boards that fail to meet performance standards, compromising their reliability. It's essential to familiarize oneself with industry standards and ensure that all specifications are rigorously followed to achieve optimal results in circuit board production.
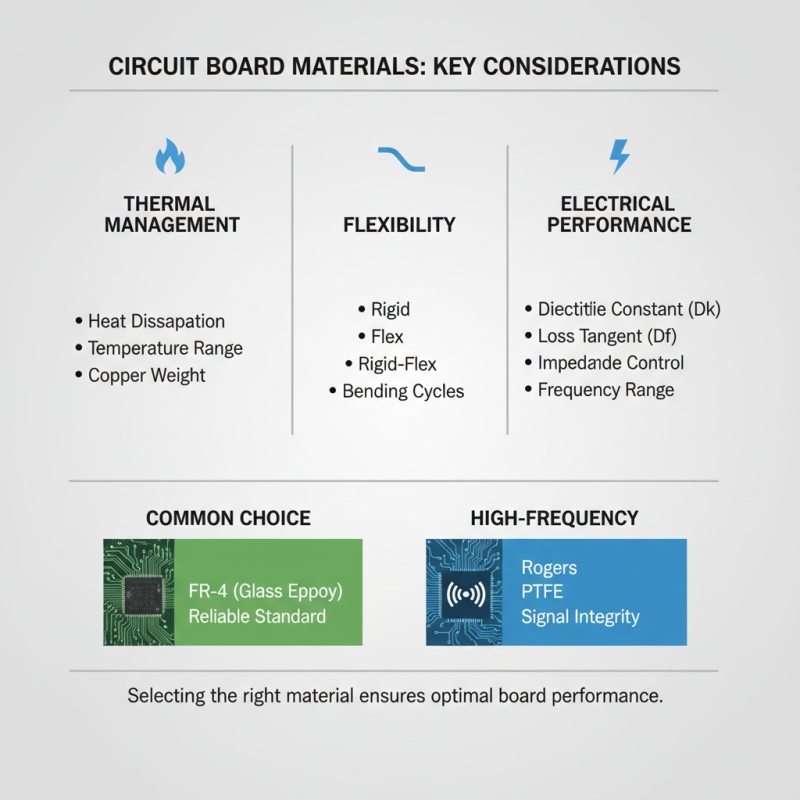
When choosing the right material for your circuit boards, it’s crucial to consider factors such as thermal management, flexibility, and electrical performance. For most applications, FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, serves as a reliable standard due to its excellent dielectric properties and mechanical strength. However, for high-frequency applications, materials like Rogers or PTFE may be required to ensure signal integrity. Understanding the specific requirements of your project will help guide your material selection process.
Additionally, environmental factors should also play a significant role in your material choice. If your circuit boards will be exposed to extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals, selecting a material with enhanced thermal or chemical resistance can greatly improve their longevity and performance. For projects requiring flexibility or conformability, consider flexible materials such as polyimide or polyester, which can adapt to various shapes and configurations while maintaining effective functionality. Ultimately, carefully assessing both the electrical and physical demands of your circuit board design will lead to better outcomes and more efficient production processes.