30+ Years of Experience in PCB Design and Manufacturing
Printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) is a critical process in electronics manufacturing. This technique transforms circuit designs into functional devices. According to Dr. Emily Chen, an expert in PCBA technologies, "The future of electronics lies in efficient assembly methods." Her insight highlights the importance of innovative techniques in this field.
In assembly, precision and efficiency are paramount. Engineers often face challenges like component placement and soldering quality. These issues can lead to failures in product performance. A thorough understanding of processes like surface mount technology (SMT) is essential. Many companies struggle with optimizing these techniques, showcasing a gap in knowledge.
Moreover, the benefits of mastering PCBA include reduced costs and improved product reliability. Yet, many still overlook the significance of continuous improvement. PCB assembly isn't just a technical skill; it requires ongoing learning and adaptation. By embracing new methods, businesses can enhance their competitiveness in the market.
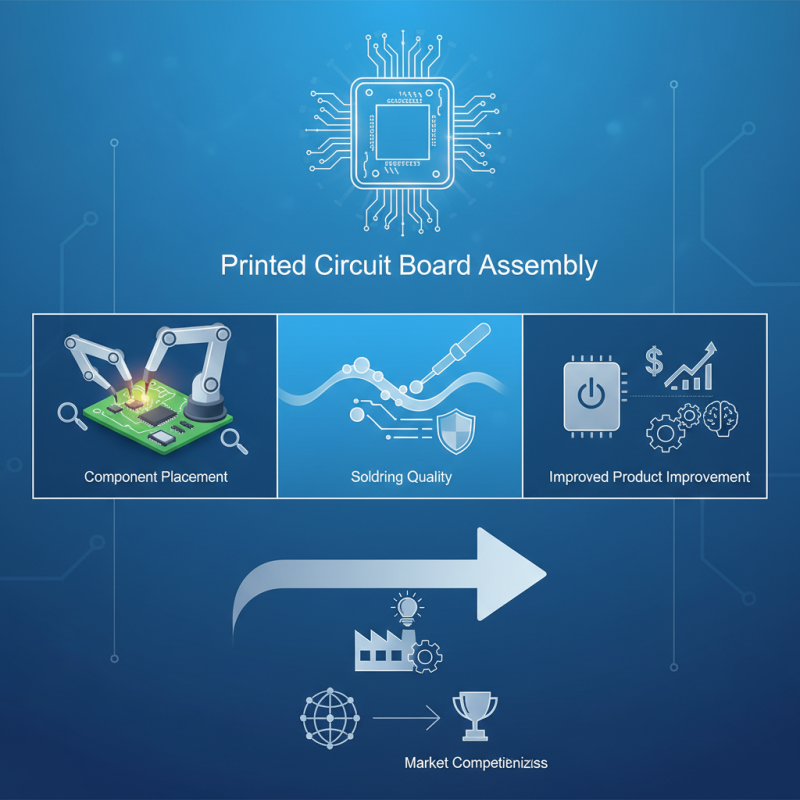
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is a critical phase in electronics manufacturing. It transforms designs into functional devices. This process involves soldering electronic components onto a circuit board. Various techniques are used for assembly, each offering unique advantages. These methods can influence the performance and reliability of electronic products.
A well-executed PCBA can reduce production costs and improve product quality. However, the assembly process can present challenges. Some common issues include misalignment of components and solder defects. These can lead to device failure. Attention to detail is crucial. Skilled operators play a vital role in ensuring accuracy. Coordination between design and assembly teams can enhance efficiency.
The benefits of PCBA are significant. Faster production times are achievable, especially with automated processes. Moreover, it allows for complex circuit designs that meet modern demands. However, it's essential to regularly review techniques. Reflecting on past assemblies can provide insights for improvement. Emphasizing quality control measures is vital for future projects.
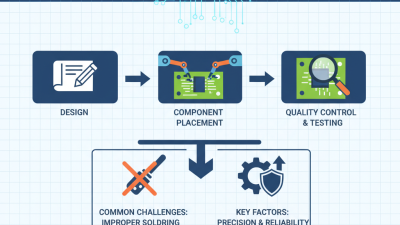
Effective PCB assembly (PCBA) relies on several key techniques. One notable method is
surface mount technology (SMT). SMT allows components to be placed directly on the surface of the printed circuit board. This technique saves space and reduces assembly time. However, precise placement is crucial. Any misalignment can lead to malfunction.
Another important technique is
through-hole technology. This involves inserting components into holes drilled in the PCB. It's more robust for heavy components but can be more time-consuming. Balancing both methods often requires careful consideration. It's not uncommon for assembly professionals to encounter issues with
soldering quality.
Quality control is essential to address these challenges.
Additionally, automated assembly tools improve efficiency. They speed up the entire process but may involve a steep learning curve. Human oversight is still needed to ensure accuracy. Sometimes, automated systems can overlook minor defects, which could impact functionality. It's vital for teams to continuously refine their processes, seeking ways to enhance both speed and quality in PCBA methods.

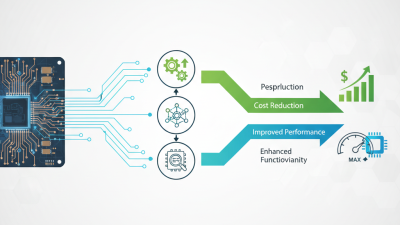
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) offers several advantages in electronics manufacturing. The global PCBA market is expected to grow significantly, with a projected value reaching $98 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the rising demand for high-quality electronics. Utilizing PCBA can lead to improved efficiency in the production process.
One key benefit of PCBA is its ability to reduce assembly time. By integrating various components onto a single board, manufacturers can streamline their workflow. Reports indicate that PCBA can decrease production time by up to 30%. Faster assembly means quicker time-to-market for new products. However, achieving this efficiency requires careful planning and quality control. Errors in assembly can lead to costly delays.
Additionally, PCBA enhances product reliability. With a compact design, electronic devices can function better under various conditions. Studies show that PCB designs can improve thermal management, reducing the risk of overheating. This is critical as devices become more powerful and compact. Yet, not all designs will succeed. Continuous evaluation and adjustment are necessary to ensure optimal performance.

PCB assembly can be a challenging process. Common issues include misalignment, solder paste defects, and component placement errors. These problems can lead to costly rework and delays. Misalignment often occurs during the automated assembly process. Even slight shifts can cause major functionality issues. It’s essential to ensure that components are precisely placed.
Solder paste defects are another frequent challenge. Too much or too little paste can result in poor connections. This may lead to short circuits or open circuits. Regular inspections are necessary to catch these issues early. A well-calibrated solder printer can help maintain consistent paste application. Additionally, training operators on handling techniques is vital.
Component placement errors frequently occur in complex assemblies. Components can easily be placed incorrectly, leading to malfunction. One way to combat this is using vision systems for verification. These systems can check whether components are in the right position. Manual oversight can also be beneficial. Regular checks and a slower workflow can help avoid mistakes. Continuous improvement will enhance the overall assembly quality.
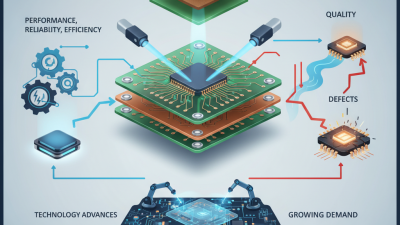
The landscape of PCB assembly is evolving rapidly. Advances in technology drive significant changes. Automation is becoming more common, allowing for faster production times and reducing human error. Machines can now handle intricate designs and high-volume production with ease. Yet, this shift raises questions about workforce implications and the need for skilled labor.
Alongside automation, additive manufacturing is gaining traction. 3D printing enables the creation of complex structures that traditional methods cannot achieve. This technology offers flexibility and reduces material waste, though it requires precise calibration and testing. Companies must adapt quickly to integrate these tools effectively.
As these trends unfold, sustainability becomes a central focus. Eco-friendly materials and processes are now essential considerations in PCB assembly. However, the challenge lies in balancing innovation with environmental impact. The industry must reflect on its practices to foster true sustainability while meeting growing demands. Embracing change is crucial, but constant evaluation and adaptation will be necessary for future success.